How the docker network works
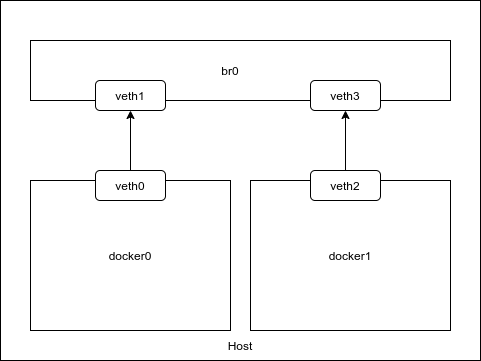
Like namespaces and cgroups the Linux kernel offers virtual ethernet device pairs and virtual bridge. Yes! you’re right, we can connect one ethernet device to the container and the other ethernet device to the bridge. After all, we can assign IP addresses and ping. Docker uses a library called llibnetwork for this.
How the Kubernetes network works
What is CNI?
CNI (Container Network Interface), a Cloud Native Computing Foundation project, consists of a specification and libraries for writing plugins to configure network interfaces in Linux containers, along with a number of supported plugins. CNI concerns itself only with network connectivity of containers and removing allocated resources when the container is deleted. Because of this focus, CNI has a wide range of support and the specification is simple to implement.
The plugin can work as an individual executable and it can invoke other plugins as well. JSON config file used to configure plugins.
Calico
Calico is a network policy engine for Kubernetes. It is designed to simplify, scale, and secure cloud networks and it integrates with Kubernetes through a CNI plug-in built on a fully distributed, layer 3 architecture. With Calico, you can implement network segmentation and tenant isolation.
Flannel
Flannel is relatively easy to install and configure. It is better for inter-container and inter-host networking. Flannel configures a layer 3 IPv4 overlay network and Flannel is suitable for most basics use cases.
Weave Net
Weave Net create a mesh overlay network between each of the nodes in the cluster, allowing for flexible and intelligent routing. Weave also provide network police feature, it automatically installed and configured when set up it. Weave good for feature reach networking without complex configuration.